HTML specification has defined what kind of content an element can contains. These specified rules are called content models.
Each HTML element can fall into zero, one, or more content models. From the content model we can also determine the location and sequence of elements in the document.
Content model types
In HTML5, there are seven content models-
- Metadata content
- Flow content
- Sectioning content
- Heading content
- Phrasing content
- Embedded content
- Interactive content
Metadata Content
Metadata content is responsible for setting up the presentation (look) or behavior to the rest of the HTML page. It can also set up the relationship of the HTML document with other documents.
The HTML elements that can contain metadata content are-
| Base, command, link, meta, noscript, script, style, title |
You can learn detail about these elements in Meta Element lesson.
Flow Content
Most contents of HTML document are in this type. These contents influence other contents to flow.
The HTML elements that can contain flow content are-
| a, abbr, address, area (if it is a descendant of a map element), article, aside, audio, b, bdi, bdo, blockquote, br, button, canvas, cite, code, command, datalist, del, details, dfn, dialog, div, dl, em, embed, fieldset, figure, footer, form, h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, header, hgroup, hr, I, Iframe, img, input, ins, kbd, keygen, label, map, mark, math, menu, meter, nav, noscript, object, ol, output, p, pre, progress, q, ruby, s, samp, script, section, select, small, span, strong, style (if the scoped attribute is present), sub, sup, svg, table, textarea, time, u, ul, var, video, wbr, text |
Sectioning Content
Sectioning content represents a section in the current document. Each sectioning content potentially has a heading content and footer.
The HTML elements that can contain sectioning content are-
| article, aside, nav, section |
Heading Content
Heading content is the titles or headers of a section in the document.
The HTML elements that can contain heading content are-
| h1,h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, hgroup |
Phrasing Content
Phrasing content is the text that you see in the document and in the HTML elements that mark up texts at the intra-paragraph level. Runs of phrasing content make up paragraphs.
Phrasing content refers to those small pieces of texts that are surrounded by other texts. For example, links. A link is often surrounded by texts.
Element that contains phrasing content should contain either text or embedded content. Elements that contain this type of contents are inline level and must have end tag.
The HTML elements that can contain phrasing content are-
| a, abbr, area (if it is a descendant of a map element), audio, b, bdi, bdo, br, button, canvas, cite, code, command, datalist, del, dfn, em, embed, I, iframe, img, input, ins, kbd, keygen, label, map, mark, math, meter, noscript, object, output, progress, q, ruby, s, samp, script, select, small, span, strong, sub, sup, svg, textarea, time, u, var, video, wbr, Text |
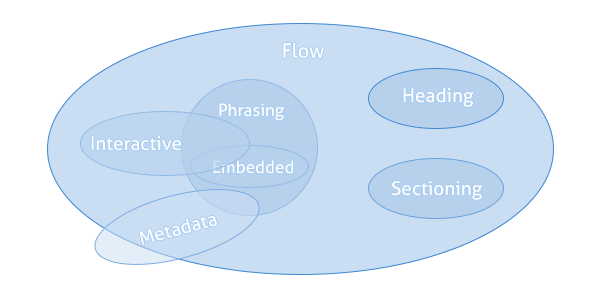
As you can see from the above picture, phrasing content is a subset of flow content. So, all phrasing contents are flow content, but the reverse is not true.
Embedded Content
Embedded content embeds resources from other sources or add contents from another mark-up languages. Example, image video etc.
The HTML elements that can contain embedded content are-
| audio, canvas, embed, iframe, img, math, object, svg, video |
Interactive Content
The contents in the web page that can interact with users are interactive content. For example, links, button etc. Interactive contents are seen inside form.
The HTML elements that can contain interactive content are-
| a, audio (if the controls attribute is present), button, details, embed, iframe, img (if the usemap attribute is present), input (if the type attribute is not in the Hidden state), keygen, label, menu (if the type attribute is in the toolbar state), object (if the usemap attribute is present), select, textarea, video (if the controls attribute is present) |
| Next Lesson : HTML Headings >> |